Teradata Architecture
Teradata provides users a centrally located architecture.Its high Level architecture(called Node) is shown below diagram.
A group of nodes forms a clique.
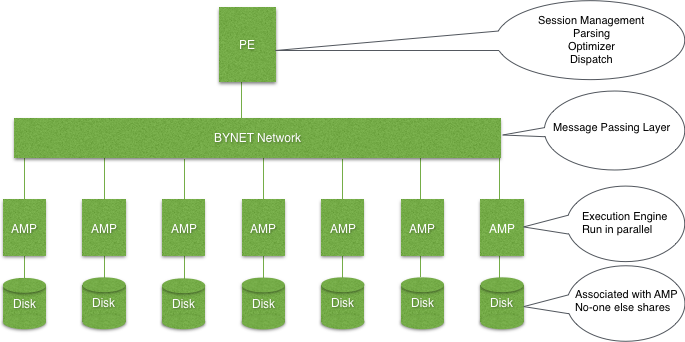
It has four main components
- Parsing Engine (PE)
- BYNET
- Access Module Processor(AMP)
- Disk
The user submits SQL to the Parsing Engine(PE). PE first checks the syntax followed by the security check and comes up with a execution plan for the AMPs. The PE communicates with the AMPs through the BYNET. The AMPs fetch data rows as needed and required per the execution plan. AMPs temporarily store the answer sets in spool space. This answer set will be then passed to user.
Parsing Engine(PE) : Four major task done by PE- Session Management.
- Checks the syntax of user requested SQL.
- Checks the security to make sure users have access to the requested table.
- Comes up with a execution plan for the AMPs to follow.
BYNET : All communication between AMPs & PE is done through the BYNET.
- There are always two BYNETs for redundancy and extra bandwidth.
- AMPs and PEs can use both BYNETs to send and retrieve data which in turn fastens the response time.